Body Type Calculator for Men & Women – Find Your Ectomorph, Mesomorph or Endomorph
Free Body Type Calculator 2026 to identify your somatotype—ectomorph, mesomorph or endomorph—and get personalized fitness and diet recommendations.
Find your body type based on your body frame and measurements
Discover whether you're an Ectomorph, Mesomorph, or Endomorph and get personalized fitness and nutrition insights.
Measure around the smallest part of your wrist
Health & Fitness Calculators
Track your health and fitness goals.
Female Body Shapes in the Fashion Industry
The fashion and fitness industries often use visual body shape categories to guide clothing design and fit recommendations. While these categories provide a helpful framework for style and fitness guidance, it's important to recognize that real human bodies exist on a spectrum with considerable individual variation.

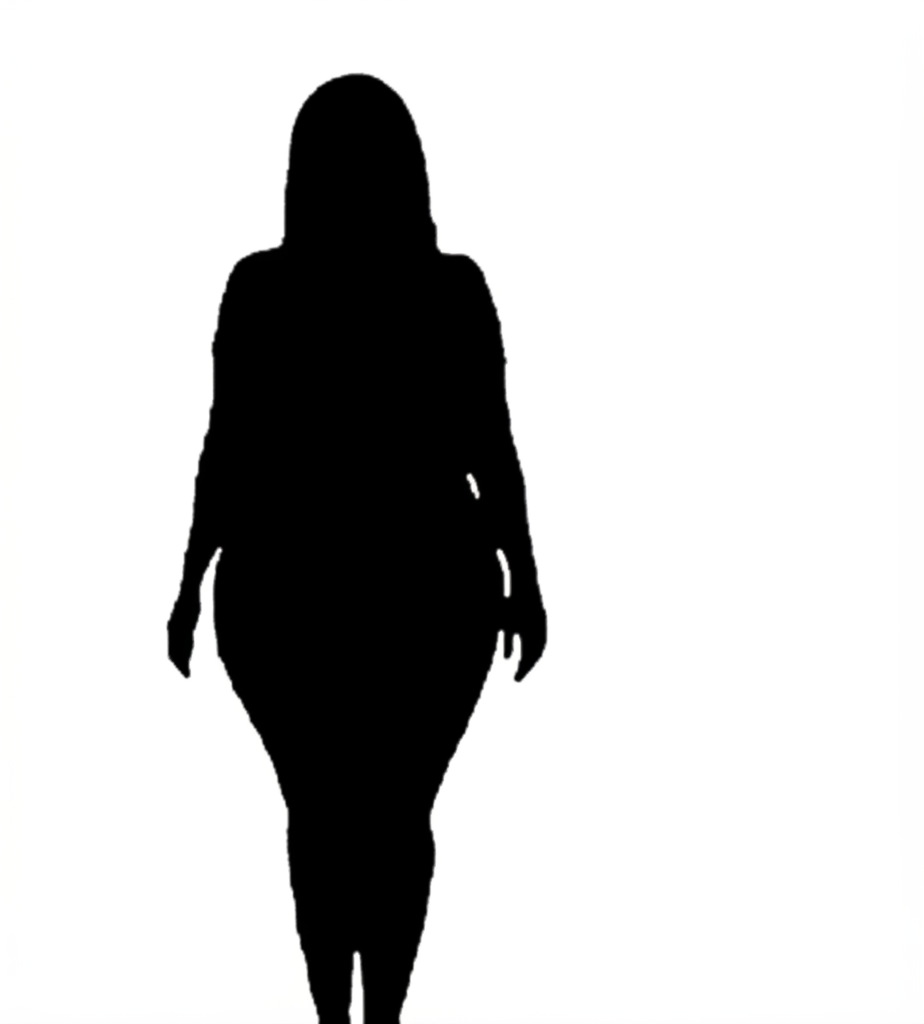
Apple (Inverted Triangle)
Apple-shaped bodies are characterized by broader shoulders and bust compared to the hips, with weight distribution concentrated in the upper body and midsection. The waist may be less defined, and the lower body appears narrower relative to the upper frame. This shape is common and often associated with higher waist-to-hip ratios.

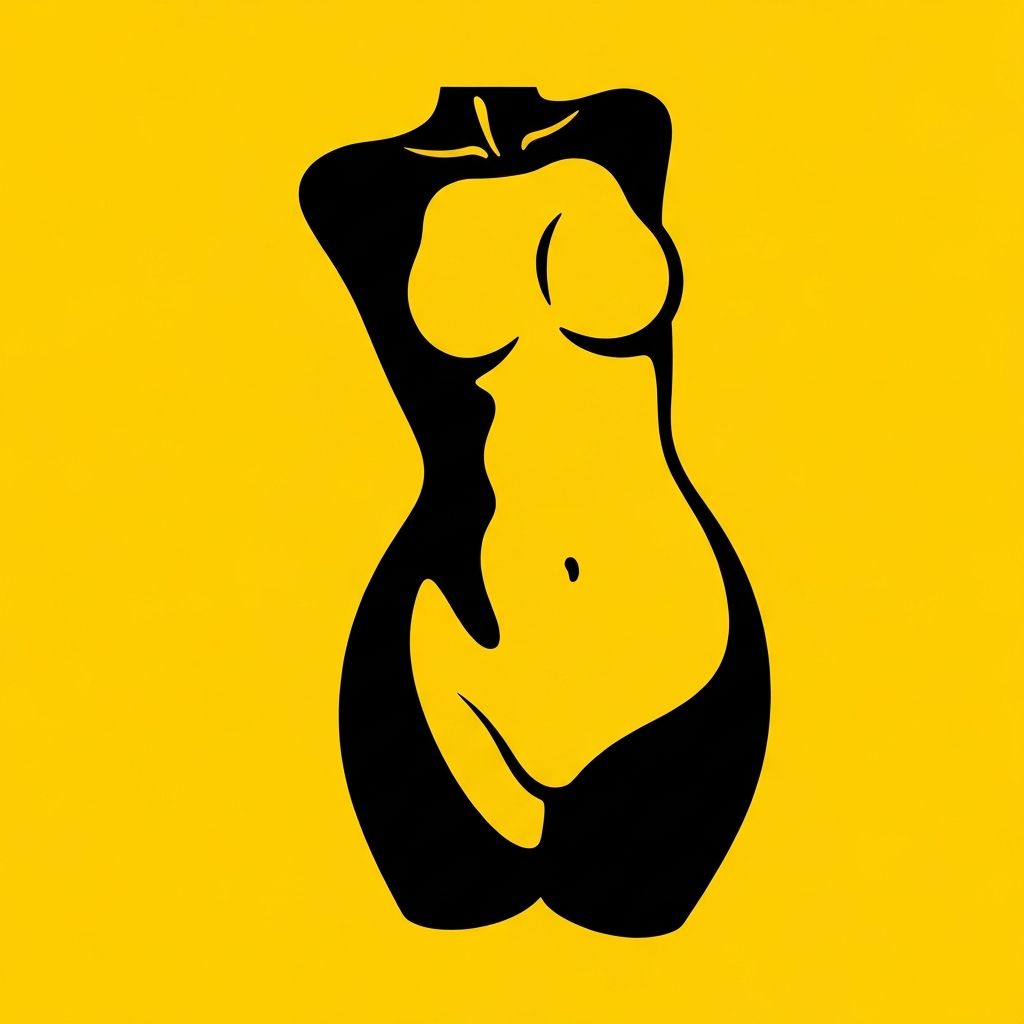
Banana (Rectangle/Straight)
Banana or rectangular body shapes have bust, waist, and hip measurements that are relatively proportional and similar in width. The body has minimal waist definition, with a straight silhouette from shoulders to hips. Large-scale research suggests this is one of the most common natural body shapes among adults globally.

Pear (Triangle/Spoon)
Pear-shaped bodies have hips that are wider than the shoulders and bust. Weight tends to be distributed in the lower body—hips, thighs, and buttocks. These shapes often have a more defined waist by comparison, creating a visually balanced silhouette.

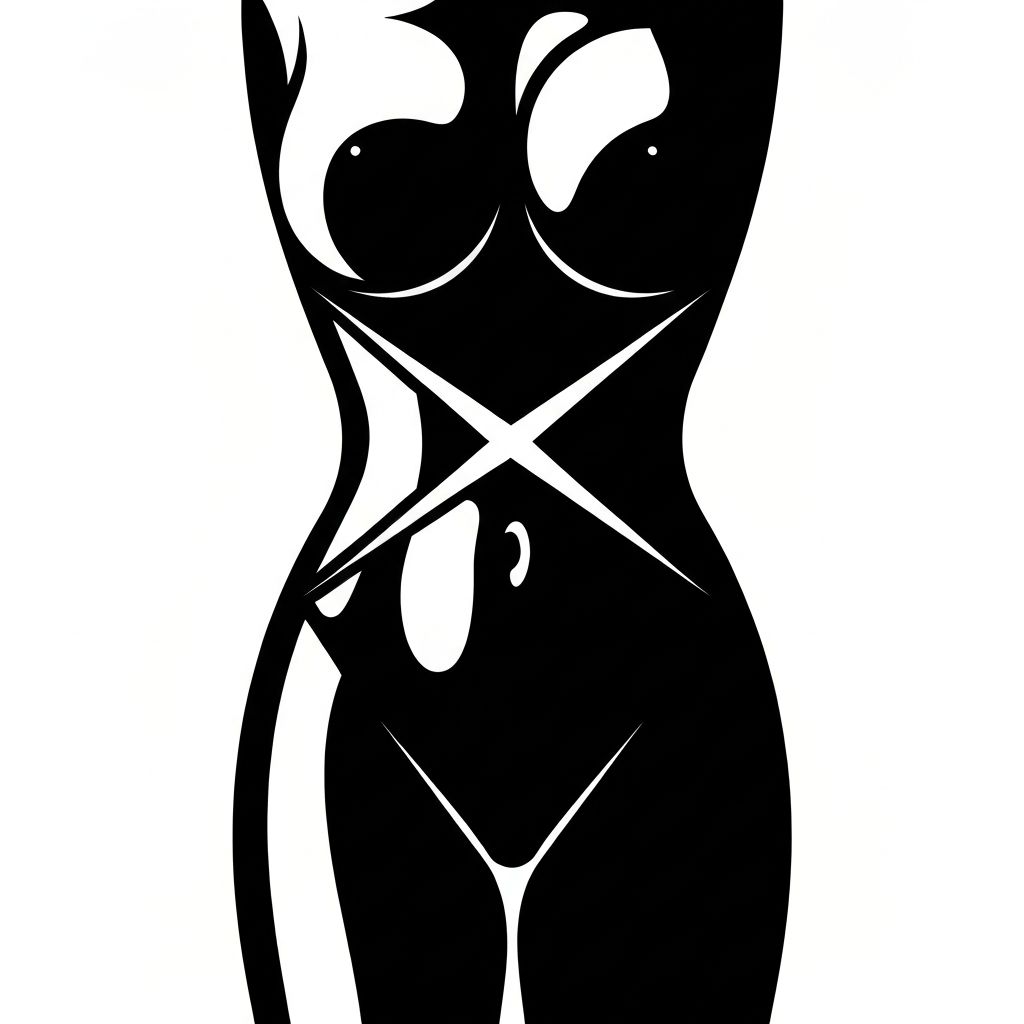
Hourglass (X Shape)
Hourglass shapes are characterized by bust and hip measurements that are nearly equal, with a narrow, well-defined waist creating symmetry. This creates an X-shaped silhouette. While historically idealized in Western culture, research indicates that classic hourglass proportions are relatively rare in the general population.

Research Note: Large-scale anthropometric studies from universities worldwide consistently show that rectangle/banana shapes are statistically most common, while true hourglasses represent a smaller percentage of the population. Most individuals have characteristics of multiple shape categories.
How Is Your Body Shape Determined?
Body shape classifications are determined primarily by proportions—the relative measurements of different body regions—rather than overall size or weight. Two people of the same weight can have different body shapes based on where their mass is distributed. Cultural standards and beauty ideals have varied dramatically throughout history and across regions, but underlying proportional relationships remain consistent.
This calculator uses established academic research and anthropometric science to classify body shapes. The classification is based on measurement ratios rather than visual assessment alone, providing more objective categorization.
Body Shape Categories Used by This Calculator
- • Hourglass: Balanced bust and hips with narrower waist
- • Bottom Hourglass: Slightly larger lower body with defined waist
- • Top Hourglass: Slightly larger upper body with defined waist
- • Spoon: Rounded lower body, tapered shoulders
- • Triangle: Wider hips than shoulders
- • Inverted Triangle: Wider shoulders than hips
- • Rectangle: Similar measurements across body
It's important to remember that not all individuals fit perfectly into one single category. Many people have characteristics that span multiple categories, and body shape is just one aspect of overall health and fitness.
Why Body Shape Matters Beyond Appearance
The waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) is calculated by dividing your waist measurement by your hip measurement. This simple number provides insight into how your body distributes fat. A higher ratio indicates more weight concentrated around the midsection, while a lower ratio suggests weight is distributed more in the hips and lower body. WHR is used alongside body shape assessment, not as a replacement for it.
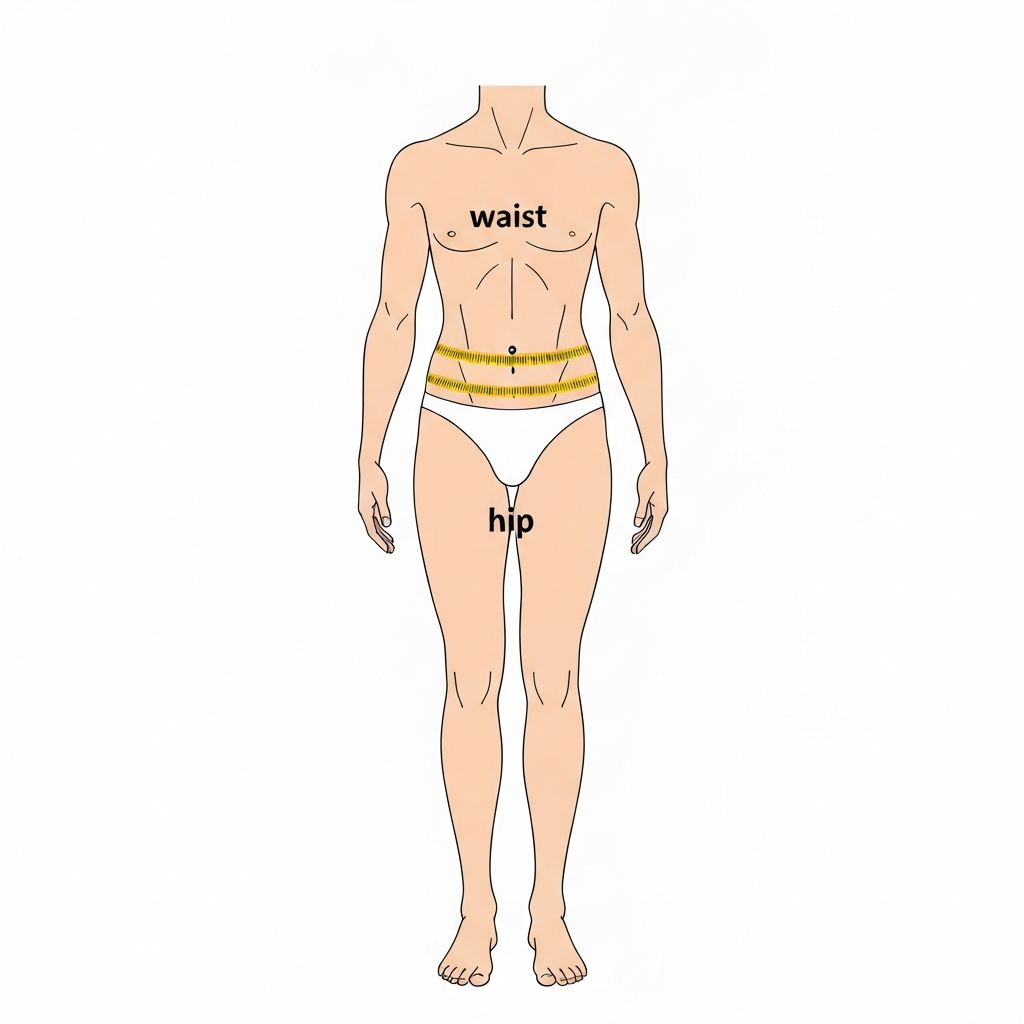
Health Insights from WHR
Research from health organizations including the WHO shows that fat location matters for health outcomes. Higher concentrations of fat in the abdominal region (higher WHR) are associated with greater metabolic risk factors including elevated blood pressure, lipid imbalances, and glucose dysregulation.
- • Apple-shaped bodies typically have higher WHR due to upper body and midsection fat distribution
- • Pear-shaped bodies generally have lower WHR with fat distributed in hips and thighs
- • WHR can sometimes identify health risks better than BMI alone, especially in older adults
WHR and Health Outcomes
The relationship between WHR and health outcomes has been extensively studied. Research indicates that optimal WHR ranges differ between men and women. Studies have linked WHR to cardiovascular health markers, metabolic function, and certain reproductive health indicators. However, WHR is one of many factors influencing health—genetics, lifestyle, diet, exercise, sleep, and stress all play significant roles.
Important: Waist-to-hip ratio is a screening tool, not a diagnostic measure. Always consult healthcare providers for personalized health assessment and recommendations.
Why Body Shape Matters Beyond Appearance
Understanding body shape goes far beyond aesthetics. Multiple practical and health-related reasons make body shape information valuable:
Clothing Fit & Comfort
Different body shapes require different clothing cuts and styles for optimal fit and comfort. Understanding your shape helps you choose garments that work with your natural proportions rather than against them.
Metabolic Function & Fat Distribution
Where your body preferentially stores fat is partly genetic. Understanding this pattern helps explain why certain areas may be more challenging to change and informs strategies for targeted health interventions.
Training & Nutrition Personalization
Different body types respond optimally to different training intensities, frequencies, and modalities. Similarly, nutritional needs and macronutrient ratios that work best can vary. Body shape is one useful variable for personalizing fitness programs.
Self-Understanding & Realistic Expectations
Knowing your body shape helps set realistic fitness and appearance goals that align with your genetic predispositions. This supports healthier mindsets and more sustainable lifestyle changes.
Key Principle: No body shape is inherently "good" or "bad." Understanding your unique body shape is about self-knowledge and optimization, not conforming to narrow ideals. All body shapes can be healthy, strong, and beautiful.
Body Type Comparison
| Characteristic | Ectomorph | Mesomorph | Endomorph |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build | Lean, thin | Athletic, muscular | Larger, rounder |
| Metabolism | Fast | Moderate | Slow |
| Weight Gain | Difficult | Moderate | Easy |
| Muscle Gain | Difficult | Easy | Moderate |
| Body Fat | Low | Moderate | Higher |
Scientific References & Sources
Our body type classifications are based on peer-reviewed research and authoritative health sources:
Healthline: Body Type Quiz & Guide
Medically reviewed somatotype information
WebMD: Body Type and Exercise
Evidence-based fitness recommendations by body type
PubMed: Somatotype and Body Composition
Peer-reviewed research on body type classification
Note: While body type theory provides a useful framework, modern research recognizes individual variation. These references support general metabolic and training principles discussed on this page.
Important Medical Disclaimer
This body type assessment is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Body type classification (somatotypes) is based on Sheldon's theory from the 1940s. While useful for general fitness guidance, it should not be used as the sole basis for health decisions.
Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider, certified nutritionist, or personal trainer before making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine.
Reviewed by Health Experts
VIP Calculator Health Team
Certified Fitness & Nutrition Specialists
Our content is reviewed by certified nutritionists and fitness professionals with credentials in exercise science, sports nutrition, and behavioral health. We base our recommendations on established scientific literature including peer-reviewed research on somatotype theory, metabolism, and body composition.
📖How to Use the Body Type Calculator
- Enter your height and wrist circumference measurements
- Select your gender for accurate assessment
- Optionally add waist and hip measurements for additional insights
- Click Calculate to determine your body type
- Review personalized fitness and nutrition recommendations
📏How to Measure Correctly
- Measure your wrist circumference at the narrowest point using a tape measure
- Measure your height without shoes in centimeters or feet
- For optional waist measurement, measure around the narrowest part of your torso
- For optional hip measurement, measure around the widest part of your hips
✨Key Features of the Body Type Calculator
- Identify ectomorph, mesomorph, or endomorph body type
- Visual body type diagrams with characteristics
- Detailed body type comparison table
- Personalized workout and diet recommendations
- Understanding of metabolic tendencies and genetics
- Downloadable body type report (PDF/TXT)
- Expert-reviewed health information (YMYL compliant)
🎯Benefits of Using the Body Type Calculator
- Optimize workouts specifically for your body type
- Choose nutrition strategies that work with your metabolism
- Understand why certain diets and exercises work better for you
- Set realistic fitness goals based on genetic tendencies
- Maximize results with a personalized fitness approach
- Learn from certified health and fitness professionals
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the three main body types?
Ectomorph (lean, difficulty gaining weight), Mesomorph (muscular, athletic build), and Endomorph (larger frame, easier to gain weight). These are called somatotypes.
Can my body type change over time?
Your genetic body type remains constant, but body composition can change significantly through diet and exercise. You can build muscle, lose fat, and transform your physique.
Is body type scientifically accurate?
Body type classification (somatotypes) was developed in the 1940s. While not a precise medical diagnostic tool, it provides a useful framework for understanding metabolic tendencies and optimizing fitness approaches.
Which body type gains muscle fastest?
Mesomorphs typically gain muscle fastest due to their naturally athletic build. However, all body types can build significant muscle with proper training and nutrition tailored to their somatotype.
Should I train differently based on my body type?
Yes, different body types respond better to specific training styles. Ectomorphs benefit from strength training, mesomorphs handle diverse training well, and endomorphs often need more cardio combined with strength work.